Substituent-dependent fluorescent sensors for zinc ions based on carboxamidoquinoline†
Abstract
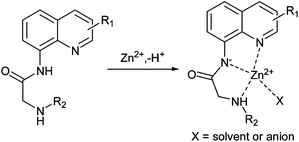
A series of carboxamidoquinoline-based fluorescent sensors (the AQZ family) were synthesized and characterized. The AQZ family members were highly soluble in

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...