Doubly bonded systems between heavier Group 15 elements†
Abstract
There has been much interest in the synthesis and properties of doubly bonded systems between heavier Group 15 elements, i. e. heavier analogues of azo-compounds (dipnictenes), from the viewpoints of fundamental and material chemistry. Although such double-bond compounds between heavier ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) PR),
PR), ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) AsR), and phosphaarsenes (RP
AsR), and phosphaarsenes (RP![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) AsR) bearing bulky substituent have been published since 1980. We have also succeeded in the synthesis of the first stable
AsR) bearing bulky substituent have been published since 1980. We have also succeeded in the synthesis of the first stable ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) SbR) and dibismuthene (RBi
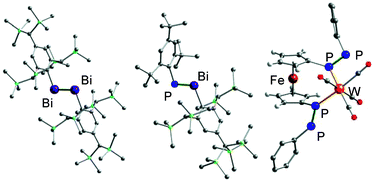
SbR) and dibismuthene (RBi![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) BiR) by taking advantage of efficient steric protection groups, 2,4,6-tris[bis(trimethylsilyl)methyl]phenyl (Tbt) and 2,6-bis[bis(trimethylsilyl)methyl]-4-[tris(trimethylsilyl)methyl]phenyl (Bbt), and revealed their structures and properties systematically. Thus, the doubly bonded compounds between heavier Group 15 elements are no longer imaginary species but are those with real existence which are stable, even in the case of the heaviest non-radioactive element bismuth, when they are appropriately protected by bulky substituents. This Perspective describes our research on the chemistry of kinetically stabilized double-bond compounds between heavier Group 15 elements.
BiR) by taking advantage of efficient steric protection groups, 2,4,6-tris[bis(trimethylsilyl)methyl]phenyl (Tbt) and 2,6-bis[bis(trimethylsilyl)methyl]-4-[tris(trimethylsilyl)methyl]phenyl (Bbt), and revealed their structures and properties systematically. Thus, the doubly bonded compounds between heavier Group 15 elements are no longer imaginary species but are those with real existence which are stable, even in the case of the heaviest non-radioactive element bismuth, when they are appropriately protected by bulky substituents. This Perspective describes our research on the chemistry of kinetically stabilized double-bond compounds between heavier Group 15 elements.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...