Electronic interactions in oligoferrocenes with cationic, neutral and anionic four-coordinate boron bridges
Abstract
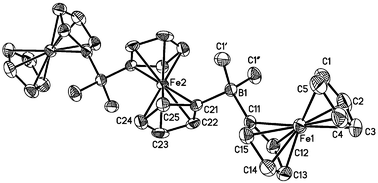
Dinuclear and trinuclear ferrocene complexes {[Fc2BMe2]Li, [Fc-BMe2-fc-BMe2-Fc]Li2, Fc2B(pyind), [Fc2B(bipy)]PF6, [Fc-B(bipy)-fc-B(bipy)-Fc](PF6)2} bearing anionic, uncharged, and cationic four-coordinate boron bridges have been synthesized (Fc: ferrocenyl; fc: 1,1′-ferrocenylene; pyind: 5-fluoro-2-(2′-pyridyl)indolyl; bipy: 2,2′-bipyridyl). The molecular structures of [Fc2BMe2]Li(12-crown-4)2, [Fc-BMe2-fc-BMe2-Fc](Li(12-crown-4)2)2, Fc2B(pyind), and [Fc2B(bipy)]PF6 were determined by X-ray crystallography. The anionic aggregates [Fc2BMe2]− and [Fc-BMe2-fc-BMe2-Fc]2− are very sensitive to air and moisture whereas bromide salts of their cationic counterparts [Fc2B(bipy)]+ and [Fc-B(bipy)-fc-B(bipy)-Fc]2+ may be dissolved in water without decomposition. Cyclic voltammograms of the diferrocene species show two well-resolved one-electron transitions separated by 0.21 V ([Fc2BMe2]Li; E°′ = −0.43 V, −0.64 V; vs. FcH/FcH+), 0.18 V (Fc2B(pyind); E°′ = −0.03 V, −0.21 V), and 0.16 V ([Fc2B(bipy)]PF6; E°′ = +0.23 V, +0.07 V), which indicates electronic interactions between the two ferrocenyl substituents. Two redox waves with an intensity ratio of 1 ∶ 2 are observed in the cyclic voltammograms of the trinuclear derivatives [Fc-BMe2-fc-BMe2-Fc]Li2 and [Fc-B(bipy)-fc-B(bipy)-Fc](PF6)2. In the case of the BMe2-bridged species, the electrochemically unique central ferrocenylene unit is oxidized at a much more cathodic potential value (E°′ = −1.21 V) than the two terminal ferrocenyl substituents (E°′ = −0.51 V). The opposite is true in the case of the B(bipy)-bridged trimer where oxidation of the terminal ferrocenyl groups (E°′ = +0.03 V) precedes oxidation of the internal iron atom (E°′ = +0.26 V). The Fe(II)/Fe(III) redox potentials of the mono- and dianionic species differ to a much larger extent from the redox potential of parent ferrocene (E°′ = 0 V) than the E°′ values of the corresponding mono- and dicationic derivatives. Apart from electrostatic interactions, the electrochemical properties of BMe2- and B(bipy)-bridged oligoferrocenes are determined by the pronounced positive inductive effect of triorganoborate substituents together with positive σ/π* hyperconjugation on the one hand and ferrocene-to-B(bipy) charge transfer on the other.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...