A new bis(3-hydroxy-4-pyridinone)-IDA derivative as a potential therapeutic chelating agent. Synthesis, metal-complexation and biological assays
Abstract
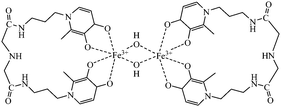
A new bis(3-hydroxy-4-pyridinone) derivative of iminodiacetic acid, imino-bis(acetyl(1-(3′-aminopropyl)-3-hydroxy-2-methyl-4-pyridinone)), IDAPr(3,4-HP)2, has been prepared and studied in its interaction with a set of hard metal ions. This tetradentate ligand presents a much higher chelating efficiency for trivalent hard metal ions (Fe, Ga, Al) than the monodentate derivative Deferriprone, namely at the diluted conditions prevailing in physiological conditions and at low clinical doses. A similar behaviour was also observed for the complexation with Zn(II) but at a significantly lower extent. This compound presents a moderate hydrophilic character at physiological pH (log D
=
−1.72). In vivo assays showed much more rapid clearance of 67Ga from most tissues of metal-loaded mice than the drug Deferriprone and the radioactivity excretion occurs mostly through the kidneys. Therefore, results from in vitro and in vivo studies indicated good perspectives for this compound to be a potential decorporating agent for hard metal ions in overload situations without depletion of essential metal ions such as zinc.
D
=
−1.72). In vivo assays showed much more rapid clearance of 67Ga from most tissues of metal-loaded mice than the drug Deferriprone and the radioactivity excretion occurs mostly through the kidneys. Therefore, results from in vitro and in vivo studies indicated good perspectives for this compound to be a potential decorporating agent for hard metal ions in overload situations without depletion of essential metal ions such as zinc.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...