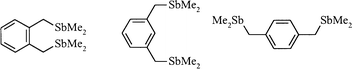
High yield syntheses for 1,2-, 1,3-, and 1,4-xylyl distibines (1,2-C6H4(CH2SbMe2)2, 1,3-C6H4(CH2SbMe2)2, 1,4-C6H4(CH2SbMe2)2, respectively) from Me2SbCl (conveniently made in situ from Me2PhSb and HClgas) and the appropriate di-Grignard are reported. The 1,3- and 1,4-phenylene distibines, 1,3-C6H4(SbMe2)2 and 1,4-C6H4(SbMe2)2, were made similarly. The new ligands have been characterised by mass spectrometry, 1H and 13C{1H} NMR spectroscopy, and by the preparation of methiodide derivatives. The crystal structures of 1,4-C6H4(CH2SbMe2)2 and [1,3-C6H4(CH2SbMe3)2]I2 have been determined. The synthesis of 1,2-C6H4(CH2SbPh2)2 has been achieved similarly in modest yield and the distibine converted into the tetra-iodo-derivative 1,2-C6H4(CH2SbPh2I2)2. The coordination modes available to these ligands have been probed by the synthesis and characterisation of complexes with nickel, iron and tungsten carbonyls. The crystal structure of [{Fe(CO)4}2{μ-1,3-C6H4(CH2SbMe2)2}] has been determined. The spectroscopic properties of these carbonyl derivatives have been compared with those of complexes of other antimony ligands, and in some cases with diphosphine and diarsine complexes, to probe the electronic properties of the new ligands.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...