1,4-Dioxobenzene compounds of aluminium
Abstract
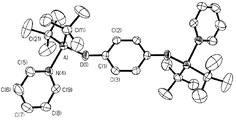
The aluminium aryloxide polymer, [{(tBu)2Al}2(μ-OC6H4O)]n (1) is synthesized by the addition of Al(tBu)3 to hydroquinone in a non-coordinating solvent, and reacts with Lewis bases, via both a solution and a solid/vapor reaction, to yield [(tBu)2Al(L)]2(μ-OC6H4O) [L = py (2), 3,5-Me2py (3) and THF (4)] via cleavage of the Al2O2 dimeric core. Thermolysis of 2–4 results in decomposition without clean formation of compound 1. However, if compound 2 is formed by the exposure of 1 to pyridine vapors, subsequent thermolysis allows for the clean solid state interconversion of compounds 1 and 2. The room temperature solid state reaction of [{(tBu)2Al}2(μ-OC6H4O)]n (1) with pyrazine (pz), 4,4′-bipyridine (4,4′-bipy) or 1,4-benzoquinone (1,4-bz) results in a rapid color change and the formation of [{(tBu)2Al}2(μ-OC6H4O)(μ-L)]n, where L = pz (5), 4,4′-bipy (6) and 1,4-bz (7).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...