Structure-guided evolution of carbonyl reductase for efficient biosynthesis of ethyl (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenylbutyrate†
Abstract
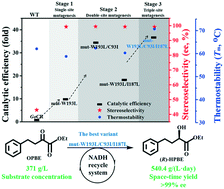
Ethyl (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenylbutanoate ((R)-HPBE) is an important versatile intermediate for the synthesis of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Herein, a structure-guided rational design was adopted to improve the catalytic performance of carbonyl reductase from Gluconobacter oxydans (GoCR) for efficient production of (R)-HPBE at high substrate loading. To enhance the catalytic performance of GoCR, three sites (Cys93, Ile187 and Trp193) were identified based on a computational approach. Through single-site and cooperative mutation at these three sites, four variants with simultaneous increase in stereoselectivity and catalytic efficiency were obtained. Variants mut-W193L, mut-W193L/C93I, mut-W193L/I187L and mut-W193L/C93I/I187L exhibited 9.8- to 37.0-fold increase in catalytic efficiency (kcat/Km) compared to the wild-type enzyme. Meanwhile, the stereoselectivities of these variants were improved from 43.0% ee of wild-type GoCR to >99% ee. In addition, mut-W193L/C93I/I187L displayed improved thermostability simultaneously. Theoretical structural analysis revealed that the changes in the catalytic pocket microenvironment resulted in the concurrent improvement of enzyme activity and thermostability. In the batch production of (R)-HPBE, up to 371 g L−1 substrate loading was completely reduced by utilizing the most efficient variant mut-W193L/C93I/I187L at 40 °C, affording (R)-HPBE with >99% ee and a space–time yield of 540.4 g L−1 per day. This study provides a potential and attractive biocatalyst for the efficient synthesis of (R)-HPBE.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...