Creation of CuOx/ZSM-5 zeolite complex: healing defect sites and boosting acidic stability and catalytic activity†
Abstract
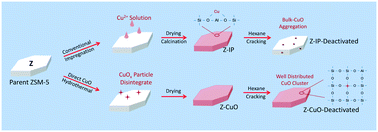
Modifying zeolite with metal by conventional methods (i.e. impregnation) could produce extra Lewis acidic species (LAS) but at the expense of intrinsic Brønsted acidity (BAS), which affects acid catalytic capability; meanwhile, other inherent problems such as metal leaching, sintering and framework Al removal are sticky issues. In this work, a simple and effective method was carried out to synthesize CuOx/ZSM-5 complex (designed as Z-CuO) by directly transforming CuO nanoparticles into ZSM-5 zeolite in cluster form. The benefits of CuOx clusters in zeolite to the acidic structure and stability of ZSM-5 zeolite are demonstrated, showing excellent performance in the hexane cracking reaction. Specifically, nano CuO can be hydrothermally disintegrated into CuOx clusters, connecting with the defective silanols inside zeolite. The doped CuOx clusters in ZSM-5 zeolite can generate extra LAS without lessening its intrinsic strong BAS, improve acidic and structural stability due to healing of the defective sites, and also protect framework Al from removal. In turn, the Z-CuO complex enhances the stability of CuOx clusters with no Cu leaching and sintering under a high-temperature reaction and catalyst regeneration. Finally, Z-CuO performs superhigh hexane conversion and exhibits high selectivity to light olefins and a long catalytic lifetime due to the stable BAS and the defect healing in Z-CuO coupled with extra LAS, leading to suppression of coke deposition.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...