Nanostructured iron oxides stabilized by chitosan: using copper to enhance degradation by a combined mechanism†
Abstract
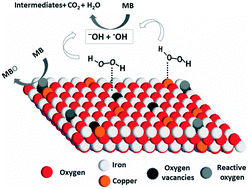
In the present study, chitosan-stabilized iron oxide (CSFe) materials were synthesized, and Cu2+ ions were introduced to the CSFe materials by isomorphic substitution (CSFeCu5, CSFeCu10, CSFeCu15). The beads were subjected to thermal treatments under a N2 atmosphere. Chemical, morphological and structural characterizations of materials was performed using different analyses. The in situ isomorphic substitution of Fe by Cu ions was observed mainly by using Mössbauer spectroscopy. The catalytic potential of the materials was evaluated by O2 evolution and methylene blue (MB) degradation tests. The H2O2 decomposition profile suggests a combined mechanism of H2O2 activation with a predominance of vacant sites. The catalytic activity of the substituted materials (CSFeCux) for degrading MB was higher than that of the unsubstituted material (CSFe). The CSFeCu10 material, in which 10% of Fe3+ is substituted by Cu2+ (mol/mol ratio), was able to degrade more than 92% of the model dye after the experimental variables were optimized. The isomorphically substituted catalysts are shown to be more stable with respect to the release of the Fe and Cu active phases, indicating that the catalytic process occurs exclusively in a heterogeneous phase. Studies on the lifetime of the composite indicate the possibility of using the isomorphically substituted catalysts in different consecutive cycles, showing that significant catalytic activity loss did not occur. Thus, incorporating Cu in the CSFe beads results in a promising material for oxidizing organic contaminants due to the robustness and catalytic activity of the resulting materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...