D–π–A-type triphenylamine dye covalent-functionalized g-C3N4 for highly efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution†
Abstract
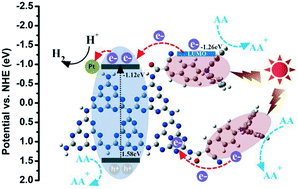
Two novel covalent bond photocatalysts, namely, g-C3N4NSs/TC1 and g-C3N4NSs/TC2 were prepared for the first time via the generation of an amide covalent bond between g-C3N4 nanosheets (g-C3N4NSs) and acyl chloride synthesized from triphenylamine-type dyes, 2-cyano-3-(4-(diphenylamino)phenyl)acrylic acid (TC1) or 3,3′-(4,4′-(phenylazanediyl)bis(4,1-phenylene))bis(2-cy-anoacrylic acid) (TC2). The experimental results indicated that triphenylamine D–π–A-type organic dye moieties covalently bonded to g-C3N4 successfully and the spectral response regions of both g-C3N4NSs/TC1 and g-C3N4NSs/TC2 could be extended from ∼460 nm to more than 600 nm. Due to the introduced amide covalent bond, the constructed g-C3N4NSs/TC1 photocatalyst showed remarkably enhanced H2 evolution activity with about 73 555.8 μmol h−1 g−1 and exhibited high apparent quantum yields (AQY) of 35.2%, 27.1%, 16.9% and 5.4% at 420 nm, 500 nm, 520 nm and 600 nm monochromatic light, respectively. Compared with the results for pure g-C3N4 NSs, about 100 times higher H2 production rate and 978 times higher AQY value were obtained for g-C3N4NSs/TC1 with the amide covalent bond under visible light irradiation. Compared to g-C3N4NSs/TC1, g-C3N4NSs/TC2 exhibited slightly lower H2 evolution activity with about 70 986.8 μmol h−1 g−1. Combining the experimental and density functional theory (DFT) calculation results, a possible mechanism can be conjectured that the electronic and geometric structures of g-C3N4NSs/TC1 are more conducive to the charge separation and the unidirectionality of electron transport in the excited state than those of g-C3N4NSs/TC2. The research reveals that this introduction of simple triphenylamine-type dyes into the surface of g-C3N4via covalent links results in a strong covalent interaction between functionalized moieties and g-C3N4 to synergistically improve the electronic and optical properties and photocatalytic performance. The present work highlights the potential use of organic dye covalent-functionalized g-C3N4via post modification as a novel photocatalyst in applications such as H2 production.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...