Unravelling the mechanism of the organocatalyzed aminolytic kinetic resolution of α-nitroepoxides: a theoretical study†
Abstract
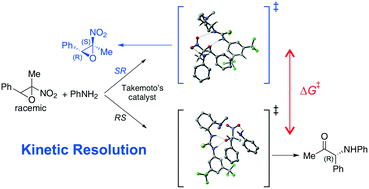
The aminolytic kinetic resolution of 2-methyl-2-nitro-3-phenyl oxirane with aniline was investigated by quantum chemical computations. It has been assessed that the reaction proceeds via a concerted ring opening/elimination of nitrous acid mechanism. The results are in agreement with the experimental findings when using the Takemoto's catalyst, which is estimated to perform in a highly efficient manner in the kinetic resolution of this class of epoxides in the absence of any background reaction. H-Bonding, π–π and CH/π interactions appear to make a significant contribution to the formation of a ternary complex and a transition state, which preferentially facilitates the reaction of the (2R,3S)-nitroepoxide to the α-amino ketone, leaving (2S,3R)-nitroepoxide unreacted.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...