Oxidative desulfurization in diesel via a titanium dioxide triggered thermocatalytic mechanism†
Abstract
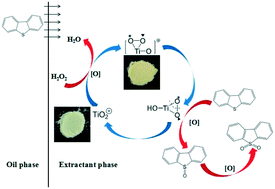
TiO2 was prepared through a sol–gel method as the thermo-catalyst for oxidative desulfurization (ODS), and H2O2 was selected as the oxidant. The morphology and structure of the catalysts were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffractometry (XRD) and UV-vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy, etc. Meanwhile, the effects of the reaction temperature (T), molar ratio of H2O2/DBT (O/S) and catalyst dosage were systematically investigated. The removal rate of DBT was 99.6% under optimal conditions. The thermocatalytic mechanism over TiO2 for oxidative desulfurization was also studied.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...