Carbonylation of dimethyl ether over Co-HMOR†
Abstract
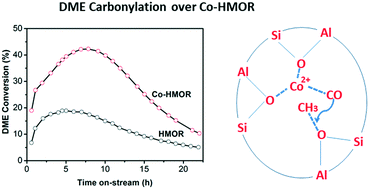
Incorporation of Co2+ into the framework of HMOR significantly enhanced the activity for the carbonylation of dimethyl ether to methyl acetate. About 68% of the Co2+ cations are located at site A in the 8-membered ring (8-MR) pores, while 32% of the metal cations are incorporated at site E of the 12-MR pores. Although the amount of the Brønsted acid sites in the 8-MR pores that are intrinsically active for DME carbonylation decreased considerably upon Co-doping, the conversion of DME increased remarkably, almost doubled. The promotional role of Co2+ in the 8-MR channels was to facilitate the adsorption/activation of both CO and DME molecules. Meanwhile, the Co2+ cations located in the 12-MR channels effectively suppressed coke deposition and thus improved the stability of the Co-HMOR catalyst.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...