TEOA-induced in situ formation of wurtzite and zinc-blende CdS heterostructures as a highly active and long-lasting photocatalyst for converting CO2 into solar fuel†
Abstract
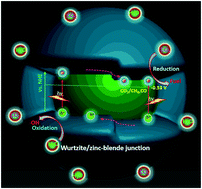
Herein, the wurtzite and zinc-blende CdS heterostructures were designed and in situ synthesized by tuning triethanolamine (TEOA) usage amount under a mild hydrothermal condition. The as-prepared samples were systematically characterized by XRD, SEM, TEM, UV-vis DRS, XPS, PL, and Mott–Schottky analysis. It is realized that a further increase in the usage amount of TEOA promotes the CdS phase transformation from hexagonal wurtzite to cubic zinc-blende during the hydrothermal process, and detailed investigations indicate that the heteronanoparticles possess explicit heterointerfaces, strong light absorption, and tunable band gaps. Especially, when used as a photocatalyst towards the reduction of CO2 to CO and CH4 in the presence of H2O, the heterostructured CdS hybrids display not only a better photocatalytic CH4-/CO-producing activity under visible-light irradiation than isolated CdS phase, but also unprecedented cycling stability without deactivation over 100 h. According to the physicochemical characterization, the remarkable improvement of photoactivity and stability over the CdS-based hybrid can be attributed to better electron–hole pair separation and migration owing to the junctions formed by the coexistence of wurtzite and zinc-blende in the CdS nanohybrids. Moreover, the role of the junctions endowed by wurtzite/zinc-blende CdS in the process of the CO2 photoreduction is evaluated using transient photocurrents and electrochemical impedance spectra (EIS) analysis, illustrating its fast-interfacial charge transfer. This study would provide a significant avenue towards effective photocatalytic conversion of CO2 using rationally designed CdS-based surface phase junction engineering at the nanoscale.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...