Highly-oriented one-dimensional MOF-semiconductor nanoarrays for efficient photodegradation of antibiotics†
Abstract
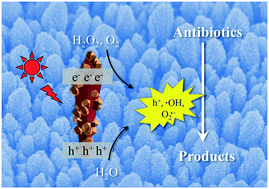
The ineffective removal of antibiotics from the aquatic environment has raised serious problems, including chronic toxicity and antibiotic resistance. Among the numerous strategies, photocatalytic degradation appears to be one of the promising methods to remove antibiotics. Semiconductors are the most widely used photocatalysts, whereas, their efficiencies still suffer from limited light absorption and poor charge separation. Given their exceptional properties, including a superior surface area and massive active sites, MOFs are excellent candidates for the formation of hierarchical nanostructures with semiconductors to address the above issues. In this study, highly-oriented one-dimensional (1D) MIL-100(Fe)/TiO2 nanoarrays were developed as photocatalysts for the first time (MIL = Materials Institute Lavoisier). The 1D structured TiO2 nanoarrays not only enable the direct and enhanced charge transport, but also permit easy recycling. With the in situ growth of MIL-100(Fe) on the TiO2 nanoarrays, the composite exhibits enhanced light absorption, electron/hole separation, and accessibility of active sites. As a result, up to 90.79% photodegradation efficiency of tetracycline, a representative antibiotic, by the MIL-100(Fe)/TiO2 composite nanoarrays was achieved, which is much higher than that of pristine TiO2 nanoarrays (35.22%). It is also worth mentioning that the composite nanoarrays demonstrate high stability and still exhibit high efficiency twice that of the pristine TiO2 nanoarrays even in the 5th run. This study offers a new strategy for the degradation of antibiotics by using 1D MOF-based nanocomposite nanoarrays.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
