Multidirectional-charge-transfer urchin-type Mo-doped W18O49 nanostructures on CdS nanorods for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution†
Abstract
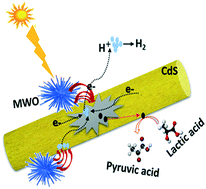
Transition metal oxides (TMOs) have attracted attention because they provide eco-friendly ways of collecting solar energy and are more stable than sulfides or phosphides for photoirradiation over long periods without photocorrosion. Among TMOs, tungsten oxides have attracted considerable attention owing to their excellent electron transport properties and good resilience to photocorrosion in aqueous media. However, pristine WO3 exhibits low photocatalytic activity because of the rapid recombination of its photogenerated charge-carriers and its narrow photo-absorption range. Consequently, the monoclinic oxygen-deficient (WO3−δ) material W18O49 (≅WO2.73) has attracted greater interest than typical tungsten oxides due to its high chemical stability and large number of oxygen vacancies (OVs). In particular, the water splitting efficiency of W18O49 is enhanced by doping with Mo, which modifies the intrinsic chemical properties of W18O49 without disturbing the crystal structure while producing more active sites. Furthermore, by tuning the morphology of Mo-W18O49 (MWO), the photocatalytic activity of MWO-embedded CdS was greatly enhanced by the very large surface area and supplementary active sites. To that end, we developed an urchin-type MWO cocatalyst integrated into CdS nanorods (NRs) by simple methods. The catalyst exhibits an enhanced production rate of H2 (40.225 mmol h−1 g−1) under simulated solar light irradiation, which is 20 times higher than that of pristine CdS NRs. The urchin-type morphology significantly shortens charge-carrier transport distances. The oxygen deficiency and Mo dopant in the W18O49 system also improve the number of active sites, which promotes the efficient utilization of light, excellent electron-transport properties, and good resilience to photocorrosion. These properties are especially beneficial for the effective excitation and separation of charge-carriers that are directed to the reduction of protons to H2. Moreover, to the best of our knowledge, this material exhibits the best performance among reported tungsten-based oxides as a cocatalyst on CdS composites.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...