Weakened CO adsorption and enhanced structural integrity of a stabilized Pt skin/PtCo hydrogen oxidation catalyst analysed by in situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy†
Abstract
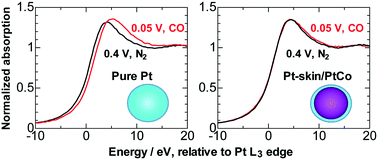
In situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy has afforded detailed structural and electronic characterization of a newly developed stabilized Pt-skin/PtCo alloy nanoparticle catalyst for CO-tolerant H2 oxidation. The X-ray absorption near-edge structure (XANES) results show the significant effects of H and CO adsorption on white lines for pure Pt nanoparticles, which are correlated with the depletion of the density of states (DOS) just below the Fermi level (FL) calculated with density-functional theory (DFT). In contrast, for the Pt-skin/PtCo surface, there is little effect on the XANES for either H or CO adsorption. The lack of effect is consistent with the lack of variation of the DOS near the FL. The extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) results for pure Pt nanoparticles have exhibited significant changes caused by H and CO adsorption. Such changes are suggested to be associated with the selected surface expansion of Pt atoms, as revealed from DFT-calculated radial distribution functions (RDFs). In contrast, for the Pt-skin/PtCo surface, there were negligible changes in the EXAFS, either with H or CO adsorption, which is consistent with the lack of changes in the DFT-calculated RDF. Notably, the rigidity of the Pt skin and the lower degree of overlap between Pt and CO orbitals, due to the narrowing of the d-band, are thought to be responsible for the weak adsorption.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...