Repurposing designed mutants: a valuable strategy for computer-aided laccase engineering – the case of POXA1b†
Abstract
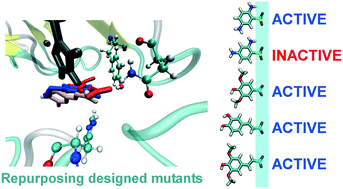
The broad specificity of laccases, a direct consequence of their shallow binding site, makes this class of enzymes a suitable template to build specificity toward putative substrates. In this work, a computational methodology that accumulates beneficial interactions between the enzyme and the substrate in productive conformations is applied to oxidize 2,4-diamino-benzenesulfonic acid with POXA1b laccase. Although the experimental validation of two designed variants yielded negative results, most likely due to the hard oxidizability of the target substrate, molecular simulations suggest that a novel polar binding scaffold was designed to anchor negatively charged groups. Consequently, the oxidation of three such molecules, selected as representative of different classes of substances with different industrial applications, significantly improved. According to molecular simulations, the reason behind such an improvement lies in the more productive enzyme–substrate binding achieved thanks to the designed polar scaffold. In the future, mutant repurposing toward other substrates could be first carried out computationally, as done here, testing molecules that share some similarity with the initial target. In this way, repurposing would not be a mere safety net (as it is in the laboratory and as it was here) but rather a powerful approach to transform laccases into more efficient multitasking enzymes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...