Surface oxygen vacancies on Co3O4 mediated catalytic formaldehyde oxidation at room temperature†
Abstract
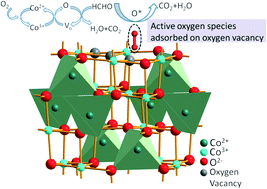
Three kinds of Co3O4 catalysts with different concentrations of surface oxygen vacancies were successfully synthesized through a solvothermal and subsequent thermolysis method. Room temperature catalytic removal of formaldehyde, which is one of the major indoor air pollutants and is seriously harmful to human health, is achieved by these Co3O4 catalysts. The existence of surface oxygen vacancies was confirmed by XPS and Raman spectroscopy. The concentration of oxygen vacancies was obtained via TGA data, which could reach 1.93% (atom ratio) in this study. H2-TPR and O2-TPD results reveal the essential role played by surface oxygen vacancies in the catalytic oxidation of formaldehyde, which is reflected in the improved mobility of oxygen and the facile formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). As a consequence, the catalytic activity shows a direct relationship with the concentration of surface oxygen vacancies. The Co3O4 nanobelts exhibited the best performance for formaldehyde oxidation due to their larger specific surface area, higher low-temperature reducibility and abundant active surface oxygen species. The high catalytic activity and stability of this Co3O4 catalyst without the introduction of noble metals as a co-catalyst shows its potential practical application for formaldehyde removal at room temperature. This study reveals the key importance of surface oxygen vacancies in the catalytic oxidation activity and complements the common viewpoint that Co3+ is the major active species in Co3O4-based systems, as well as provides a possibility for developing high performance catalysts through surface modification.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...