Realization of a highly effective Pd–Cu–Clx/Al2O3 catalyst for low temperature CO oxidation by pre-synthesizing the active copper phase of Cu2Cl(OH)3
Abstract
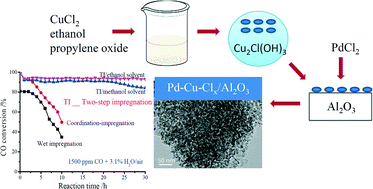
The Pd–Cu–Clx/Al2O3 catalysts (PCC) were prepared by a two-step impregnation (TI) method in organic solvent, wet impregnation (WI) method and NH3 coordination-impregnation (CI) method. The PCC-TI catalyst prepared by the two-step impregnation method (TI) exhibited much higher activity and stability for CO oxidation than the other catalysts, resulting from the smaller size of Cu2Cl(OH)3 and fewer carbonates deposited on the surface of PCC-TI catalyst. Using the PCC-TI catalyst, the complete conversion temperature of CO was 10 °C in the presence of 3.1% H2O. Among the three catalysts, the activation energy (Ea) of PCC-TI/ethanol was the lowest (27.1 kJ mol−1). The PCC-TI/ethanol prepared in ethanol solvent showed a higher activity compared with PCC-TI/methanol, due to much stronger interactions between the copper and palladium species. High concentrations of moisture and CO had a negative effect on the CO conversion. The former is due to excessive numbers of –OH groups (from H2O dissociation) which occupy the active sites of Pd and Cu, though –OH groups can work as part of the catalytic cycle, and the latter may originate from competitive adsorption and the presence of carbonates on the surface. We used DFT calculations to study the adsorption of H2O and CO on the surface, and the catalytic cycle of CO oxidation on the Pd species, revealing the possible routes for the formation of common species observed in the in situ DRIFTS spectra.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...