Gold nanoparticles supported on Ce–Zr oxides for the oxidative esterification of aldehydes to esters†
Abstract
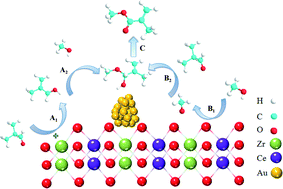
Au nanoparticles supported on Ce–Zr oxides were prepared and characterized in order to study the role of the support in the oxidative esterification of aldehydes in the presence of molecular oxygen. Ce–Zr solid solutions were synthesized by using (NH4)2Ce(NO3)6 as a precursor, while the mixed oxides were obtained by using a Ce(NO3)3 precursor. The solid solutions exhibited a smaller crystallite size, higher BET surface area, larger amount of H2 consumption, and higher acidity and basicity than the mixed oxides at the same Ce/Zr molar ratio due to the incorporation of Zr4+ into the ceria lattice. The effect of the support was investigated because all the samples presented similar Au particle sizes, as confirmed by the HAADF-STEM study. Supports with higher reducibility showed better performance by activating methanol to methoxy and facilitating the β-H elimination of hemiacetal. We also found that the formation of hemiacetal was enhanced by the acidic sites and basic sites of Au catalysts supported on solid solutions possessing similar reducibility. A plausible reaction mechanism for the oxidative esterification of aldehydes on Ce–Zr solid solution-supported Au nanoparticles was proposed. The screened catalyst was also applicable to the oxidative esterification of different benzylic aldehydes, producing high yields. This catalyst could be reused after a simple separation eight times, keeping a high selectivity of above 99%.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...