Ethanol steam reforming over Rh and Pt catalysts: effect of temperature and catalyst deactivation
Abstract
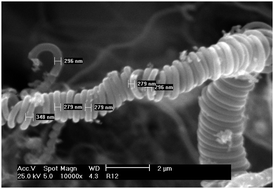
In this study 0.2% Rh/alumina and 0.2% Pt/alumina catalysts were tested for ethanol steam reforming (ESR) over a range of temperatures (773–873 K) at 20 barg with a 5 : 1 steam to ethanol ratio. Hydrogen was always the main product over Rh/Al2O3 although liquid products such as acetaldehyde, diethyl ether and acetone were also produced (<12%). Pt/Al2O3 also produced hydrogen as the main product but at 773 K significant levels of ethene were formed. Less liquid product was formed over the Pt/Al2O3 (<5%). Hydrogenation of ethene to ethane was inhibited and an activation energy comparable with low temperature studies was obtained for rhodium (∼42 kJ mol−1) however the platinum catalyst gave a low activation energy more typical of a diffusion controlled system (∼20 kJ mol−1). At 873 K the platinum catalyst is more active (90% conversion cf. ∼60%) and gives a higher hydrogen selectivity (55% cf. 49%) than the rhodium catalyst. Temperature-programmed oxidation (TPO), Raman spectroscopy, BET and SEM analysis were used to characterise the nature of the coke species for reactions at 773 K, 823 K and 873 K. The TPO results indicated that different types of coke were deposited on both catalysts during ESR. Carbon nanotubes and filamentous coke were observed on the catalysts after ESR at 873 K. Raman analysis revealed that the coke deposited on the catalysts was graphitic in nature and the disorder in the graphitic type coke generally increased with an increase in the reaction temperature.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...