Catalytically active structures of SiO2-supported Au nanoparticles in low-temperature CO oxidation
Abstract
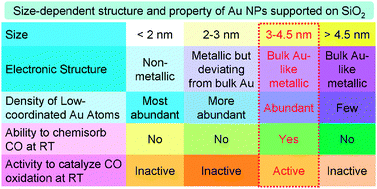
Various Au/SiO2 catalysts have been prepared by the deposition–precipitation method followed by calcination in air or reduction in H2. The structures of supported Au nanoparticles were characterized in detail by XRD, TEM, XPS, in situ XANES and operando DRIFTS of CO chemisorption, and their catalytic activity in CO oxidation was evaluated. Calcined in air, the gold precursor decomposes into Au(I) species at low temperatures and further to Au(0) at elevated temperatures, forming supported Au nanoparticles mostly larger than 4.5 nm. Reduced in H2, the gold precursor can be facilely reduced to Au(0) at low temperatures, forming supported Au nanoparticles with different size distributions depending on the reduction temperature. Supported Au nanoparticles around 3–4.5 nm with both abundant low-coordinated Au atoms and bulk Au-like electronic structure effectively chemisorb CO and catalyze CO oxidation at room temperature (RT). Larger supported Au nanoparticles with bulk Au-like electronic structure but few low-coordinated Au atoms do not chemisorb CO and catalyze CO oxidation at RT, and finer supported Au nanoparticles with abundant low-coordinated Au atoms but bulk Au-unlike electronic structure also do not chemisorb CO and catalyze CO oxidation at RT. These results provide solid and comprehensive experimental evidence that supported Au nanoparticles with both abundant low-coordinated Au atoms and bulk Au-like electronic structure are the catalytic active structures for catalyzing CO oxidation at RT without the involvement of oxide supports. The density of low-coordinated Au atoms increases with the decrease of their size, but their electronic structure eventually deviates from bulk Au-like electronic structure; therefore, the catalytic activity of SiO2-supported Au nanoparticles in low-temperature CO oxidation inevitably exhibits a volcano-shaped dependence on their size with the optimum size between 3 and 4.5 nm.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...