Carbon nitrides and metal nanoparticles: from controlled synthesis to design principles for improved photocatalysis
Abstract
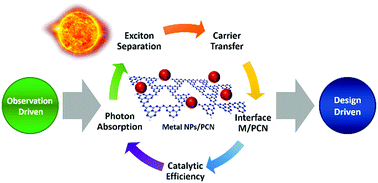
The use of sunlight to drive chemical reactions via photocatalysis is of paramount importance towards a sustainable future. Among several photocatalysts, earth-abundant polymeric carbon nitride (PCN, often wrongly named g-C3N4) has emerged as an attractive candidate due to its ability to absorb light efficiently in the visible and near-infrared ranges, chemical stability, non-toxicity, straightforward synthesis, and versatility as a platform for constructing hybrid materials. Especially, hybrids with metal nanoparticles offer the unique possibility of combining the catalytic, electronic, and optical properties of metal nanoparticles with PCN. Here, we provide a comprehensive overview of PCN materials and their hybrids, emphasizing heterostructures with metal nanoparticles. We focus on recent advances encompassing synthetic strategies, design principles, photocatalytic applications, and charge-transfer mechanisms. We also discuss how the localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) effect of some noble metals NPs (e.g. Au, Ag, and Cu), bimetallic compositions, and even non-noble metals NPs (e.g., Bi) synergistically contribute with PCN in light-driven transformations. Finally, we provide a perspective on the field, in which the understanding of the enhancement mechanisms combined with truly controlled synthesis can act as a powerful tool to the establishment of the design principles needed to take the field of photocatalysis with PCN to a new level, where the desired properties and performances can be planned in advance, and the target material synthesized accordingly.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...