2D-Pnictogens: alloy-based anode battery materials with ultrahigh cycling stability
Abstract
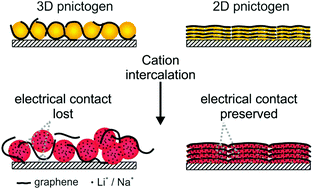
There is an increasing demand for efficient energy storage systems in our modern mobile society for a wide range of applications such as smart grids, portable electronic devices, and electric vehicles. The performance of advanced batteries in terms of energy density, power density, cyclability, and safety is mainly determined by the primary functional components, particularly by the electrode materials. Black phosphorus (BP) and the following elements in group V (pnictogens) including arsenic, antimony, and bismuth with layered structures have attracted tremendous attention to replace the graphite anode. This is due to their extremely high specific-capacities for lithium and sodium storage based on the alloying reaction mechanism; however, the same mechanism causes an irreversible volume expansion and thus low cycling stability. Since the discovery of single layer BP and its outstanding physical properties such as tunable band gap, strong in-plane anisotropy, and high carrier mobility, the battery community have intensively studied this material as well as the 2D structures of other pnictogens. In this review, first, the preparation and properties of 2D-pnictogens including crystal structure and chemical stability are briefly described. Second, the theoretical and experimental details of the intercalation and alloying mechanisms are discussed. Finally, the excellent performance of 2D-pnictogens for lithium ion and sodium ion batteries and their principal advantages compared to their parent 3D structures are presented.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...