Unique physicochemical properties of two-dimensional light absorbers facilitating photocatalysis
Abstract
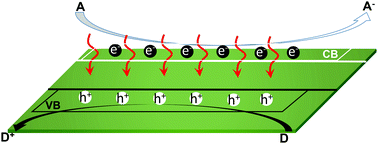
The emergence of two-dimensional (2D) materials with a large lateral size and extremely small thickness has significantly changed the development of many research areas by producing a variety of unusual physicochemical properties. Semiconductor photocatalysis is intrinsically controlled by multiple light–matter, light absorber–cocatalyst and molecular/ionic-matter interactions that can be highly dependent on the geometric features of the light absorber. In this review, we focus on the unique structures and unusual physicochemical properties of 2D semiconducting light absorbers and their roles in facilitating photocatalysis. In particular, we highlight their structure–property relationships considering the unique electronic structure, optical absorption, spatial separation of charge carriers, structural advantages as a host of active guests, and the strain-modulated band structures of the 2D light absorbers. The representative development of a number of 2D light absorbers with structural/compositional features such as nonporous and porous structures, heteroatom/defect modification and manufactured hybrid structures for photocatalysis are discussed in detail. We conclude with a discussion of some key challenges and future directions for the development of 2D photocatalysts for efficient solar energy conversion.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2D nanomaterials: beyond graphene and transition metal dichalcogenides


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
