Surface electronic states mediate concerted electron and proton transfer at metal nanoscale interfaces for catalytic hydride reduction of –NO2 to –NH2†
Abstract
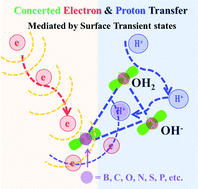
Concerted electron and proton transfer is a key step for the reversible conversion of molecular hydrogen in both heterogeneous nanocatalysis and metalloenzyme catalysis. However, its activation mechanism involving electron and proton transfer kinetics remains elusive. With the most widely used catalytic hydride reduction of 4-nitrophenol (4-NP) to 4-aminophenol (4-AP) as a model reaction, we evaluate the catalytic activity of noble metal nanoparticles (NPs) trapped in porous silica in aqueous NaBH4 solution. By virtue of a novel combination of catalyst design, reaction kinetics, isotope labeling, and multiple spectroscopic techniques, the real catalytic site for the conversion of –NO2 to –NH2 is identified to be the water–hydroxyl transition metal complex, which could further react with NaBH4 to form a new triangular configuration metal complex of H3B–water–hydroxyl with dynamic features. It yields an ensemble of surface electronic states (SESs) though space overlapping of p orbitals of one B and several O atoms (including the O atoms of 4-NP), which could act as an alternative channel for concerted electron and proton transfer. This work highlights the critical role of the conceptual SESs model in heterogeneous catalysis to tune the chemical reactivity and also sheds light on the intricate working of the [FeFe]-hydrogenases.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...