Electrochemical behavior and electrodeposition of gallium in 1,2-dimethoxyethane-based electrolytes†
Abstract
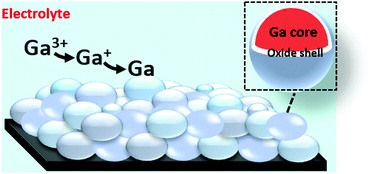
The electrochemical behavior and electrodeposition of gallium was studied in a non-aqueous electrolyte comprising of gallium(III) chloride and 1,2-dimethoxyethane (DME). Electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance (EQCM) and rotating ring disk electrode (RRDE) measurements indicate that reduction of gallium(III) is a two-step process: first from gallium(III) to gallium(I), and then from gallium(I) to gallium(0). The morphology and elemental composition of the electrodeposited layer were examined using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX). Metallic gallium was deposited as spheres with diameters of several hundred nanometers that were stacked on top of each other. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) revealed that each gallium sphere was covered by a thin gallium oxide shell. Electrochemical experiments indicated that these oxide layers are electrically conductive, as gallium can be electrodeposited and partially stripped on or from the layer of spheres below. This was further evidenced by simultaneous electrodeposition of gallium and indium, using indium as a tracer. Electrodeposition of gallium from an O2-containing electrolyte resulted in spheres with smaller diameters. This was due to the formation thicker oxide shells, through which diffusion of gallium atoms that were electrodeposited on the surface, was slower. The concentration of gallium adatoms on top of the gallium spheres to form a new sphere therefore reaches the critical concentration for nucleating a new gallium sphere sooner, leading to smaller spheres.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...