The structure of metallic melts in binary homogenous alloys: a thermodynamical understanding from the Wulff cluster model
Abstract
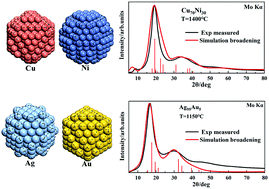
In the present work, a new liquid metal model (Wulff cluster model) which has been proved to describe the structures of pure metal melts has been extended to binary homogeneous alloy melts (Cu–Ni and Ag–Au). The shapes of the nano-particles are determined by surface energies of different families of crystal planes, calculated by density functional theory (DFT), whereas the size was given by the pair distribution function (PDF) g(r) which was converted from experimental high-temperature X-ray diffraction (HTXRD). We demonstrated that the simulated X-ray diffraction (XRD) curves from present models match the experimental results quite well at high temperatures above the liquid–solid two-phase region, including not only the position and width of the peaks but also the relative intensity of the first and second peaks. Moreover, when the temperature is near the liquid–solid two-phase region, our model also fits the experimental strength curve well after modification using the solid XRD pattern of a relatively high melting point metal instead of its nano-particle. The agreement indicates the nucleation processes in homogeneous alloy melts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...