Solution combustion synthesis, characterization, magnetic, and dielectric properties of CoFe2O4 and Co0.5M0.5Fe2O4 (M = Mn, Ni, and Zn)
Abstract
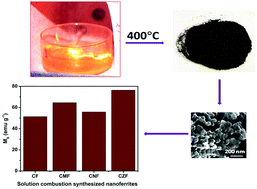
Nanocrystalline CoFe2O4 and Co0.5M0.5Fe2O4 (M = Mn, Ni, and Zn) ferrites were prepared by the solution combustion method using oxalyl dihydrazide as a fuel. These materials were characterized by several physicochemical techniques. X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns indicate the cubic spinel structure of these ferrites. Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) images demonstrate the microporous nature of the materials because of the large amount of gas production during their synthesis. High resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) images show lattice fringes corresponding to the {220} and {311} planes of the spinel structure. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra exhibit absorption bands around the 500–600 cm−1 wavenumber region which are related to metal–oxygen bonds with tetrahedral coordination. Symmetric and asymmetric stretching and symmetric bending modes associated with tetrahedral and octahedral cations present in the spinel structures have been assessed by Raman spectroscopy. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) studies demonstrate the presence of Co2+, Mn2+, Ni2+, Zn2+, and Fe3+ in tetrahedral and octahedral coordinations in these ferrites. Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 is observed to show the highest saturation magnetization among all these materials. The dielectric measurements reveal that the dielectric constant and loss values decrease with an increase in frequency and the ac conductivity increases at higher frequencies due to mobilization of the charge carriers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...