Tailoring the protonic conductivity of porous yttria-stabilized zirconia thin films by surface modification
Abstract
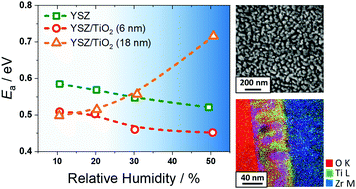
Porous yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) thin films were prepared by pulsed laser deposition to investigate the influence of specific surface area on the electronic, oxygen ion, and protonic transport properties. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy was carried out as a function of temperature, oxygen activity and humidity of the surrounding atmosphere. At high humidity, protons on the surface of the porous YSZ thin films lead to increased conductivity, even for temperatures up to 700 °C. With increasing relative humidity, the activation energy of proton transport decreases because of changes in the transport mechanism from Grotthuss-type to vehicle-type transport. By coating the porous YSZ films with an amorphous titania (TiO2) layer of only a few nanometer thickness using atomic layer deposition, the protonic contribution to conductivity is significantly reduced. Depositing an 18 nm-thick anatase TiO2 surface layer, the protonic conductivity contribution increases again, which can be attributed to enhanced capillary condensation because of the lower pore size. Interestingly, the filling of pores is accompanied by a decrease in proton mobility. Theses results demonstrate the significant effect that the porosity and the surface properties have on the protonic transport and further provide new design principles for developing nanostructured proton-conducting oxides.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...