Stabilities of group-III phosphide (MP, M = B, Al, Ga and In) monolayers in oxygen and water environments†
Abstract
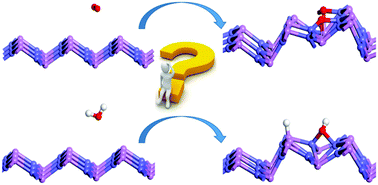
Group-III phosphide (MP, M = B, Al, Ga and In) monolayers have promising applications in photocatalysis, nanoelectronics and optoelectronics. Their stabilities in oxygen and water environments are crucial to their practical applications. In order to investigate the stabilities of the MP monolayers, density functional theory calculations combined with ab initio molecular dynamics (AIMD) simulations were performed to illustrate their interactions with oxygen and water molecules. It was found that an oxygen molecule spontaneously dissociates on the AlP, GaP and InP monolayers. In the meantime, the corresponding monolayer structures are severely distorted after annealing. In contrast, BP monolayer is stable in the oxygen environment due to a high dissociative barrier of 0.89 eV. We found that a water molecule dissociates on AlP monolayer with a dissociative energy barrier of 0.42 eV, but it can be stably adsorbed on the BP, GaP and InP monolayers without the breakage of O–H bonds. Nevertheless, with the increase of the number of water molecules, the formed intermolecular H-bonding can promote interactions between water molecules and the monolayers, leading to structural distortion in the GaP and InP monolayers. When putting a water molecule near the oxygen molecule, the oxidation barrier of the BP monolayer is reduced to 0.75 eV, which is still high enough to maintain its stable state. This investigation theoretically provides environmental conditions for the experimental fabrication and practical application of semiconductor monolayers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...