Exploring exchange processes in proteins by paramagnetic perturbation of NMR spectra†
Abstract
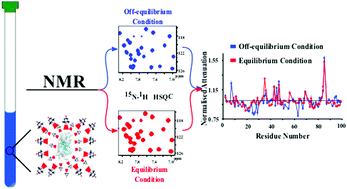
The effect of extrinsic paramagnetic probes on NMR relaxation rates for surface mapping of proteins and other biopolymers is a widely investigated and powerful NMR technique. Here we describe a new application of those probes. It relies on the setting of the relaxation delay to generate magnetization equilibrium and off-equilibrium conditions, in order to tailor the extent of steady state signal recovery with and without the water-soluble nitroxide Tempol. With this approach it is possible to identify signals whose relaxation is affected by exchange processes and, from the relative assignments, to map the protein residues involved in association or conformational interconversion processes on a micro-to-millisecond time scale. This finding is confirmed by the comparison with the results obtained from relaxation dispersion measurements. This simple and convenient method allows preliminary inspection to highlight regions where structural or chemical exchange events are operative, in order to focus on quantitative subsequent determinations by transverse relaxation dispersion experiments or analogous NMR relaxation studies, and/or to gain insights into the predictions of calculations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...