Interaction of aliphatic amino acids with zwitterionic and charged lipid membranes: hydration and dehydration phenomena†
Abstract
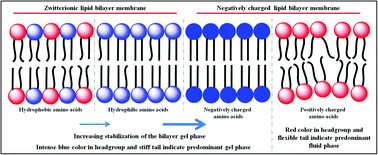
In the present contribution, we investigate the interactions of lipid bilayer membranes of different charges and different phase states with aliphatic amino acids of varying charge (aspartic acid, glutamic acid, arginine and lysine) and hydrophobicity (serine, leucine and valine) by steady state and time-resolved spectroscopic techniques, dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurements and confocal imaging (CLSM). The study reveals that negatively charged amino acids such as aspartic acid and glutamic acid interact strongly with the lipid membranes particularly with negatively charged lipid membranes by stabilizing their gel phase. On the other hand, positively charged amino acids bring in hydration in the membranes. We explain this unique observation by the shift in pKa of amino acids in the vicinity of the lipid membranes and solvation and desolvation processes in the light of recent computer simulations. We also find that hydrogen bonding plays a significant role in governing the interaction of aliphatic amino acids with zwitterionic lipid membranes. The more polar serine bearing a hydroxyl group at the terminal carbon offers a stronger interaction with the lipid bilayer membranes as compared to its analogues leucine and valine, which are hydrophobic in nature.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2020 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...