The primary photo-dissociation dynamics of amino acids in aqueous solution: breaking the Cα-bond†
Abstract
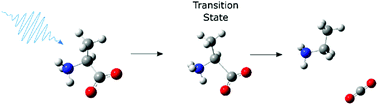
We report a study of the primary photo-dissociation dynamics of aqueous alanine, isoleucine and proline by 200 nm UV pump–IR probe transient absorption spectroscopy. Photo-dissociation of the three amino acids predominantly results in decarboxylation, and 38 ± 7% of the excited alanine, 35 ± 10% of the excited isoleucine and 47 ± 10% of the excited proline zwitterions remain dissociated 100 picoseconds after the excitation. The decarboxylation occurs from a transient intermediate with a lifetime of ∼20 picoseconds to which we assign the excited state of the amino acids based on comparison of the measured and calculated IR spectra, and calculated excited state energy surfaces.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...