Tunable helical structures formed by ABC triblock copolymers under cylindrical confinement
Abstract
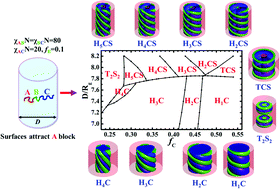
Block copolymers confined in nanopores provide unique achiral systems for the formation of helical structures. With AB diblock copolymers, stable single and double helical structures are observed. Aiming to obtain more different helical structures, we replace the AB diblock copolymer with linear ABC triblock copolymers. We speculate that a core–shell superstructure is formed within the nanopore, which is composed of a C-core cylinder wrapped by B-helices within the A-shell. Accordingly, the pore surface is set to be most attractive to the majority A-block and a typical set of interaction parameters is chosen as χACN ≪ χABN = χBCN = 80 to generate the frustrated interfaces. Furthermore, the volume fraction of B-block is fixed as fB = 0.1 to form helical cylinders. A number of helical structures with strands ranging from 1 to 5 are predicted by self-consistent field theory, and in general, the number of strands decreases as the volume fraction of C-block fC increases in a given nanopore. More surprisingly, the variation of helical strand in the confined system has an opposite trend to that in the bulk, which mainly results from the constraint of the cylindrical confinement on the change of the curvature between the outer A-layer and the inner B/C-superdomain. Our work demonstrates a facile way to fabricate different helical superstructures.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2019 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...