Cooperativity effect of the π⋯π interaction between drug and DNA on intercalative binding induced by H-bonds: a QM/QTAIM investigation of the curcumin⋯adenine⋯H2O model system†
Abstract
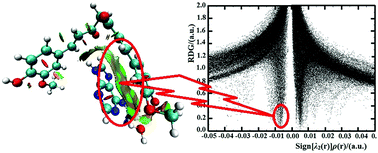
In order to reveal the nature of intercalative binding of drug to DNA, the cooperativity effect of the π⋯π interaction was investigated in the curcumin⋯adenine⋯H2O model system by applying a combined QM and QTAIM computational approach. The H-bonds between the electron-donating group of curcumin and adenine induce the formation of the π⋯π stacking. The introduction of H2O weakens the H-bonding and π⋯π interactions, leading to an anti-cooperativity effect, as is confirmed by the AIM (atoms in molecules) and RDG (reduced density gradient) analysis. Thus, it can be inferred that the anti-cooperative effect is the main driving force for the intercalative binding of drug to DNA bases, which is in agreement with many experimental phenomena. Therefore, the designed DNA-targeted intercalating drugs should possess not only hydrophobic moieties, but also strong electron-donating groups bound to the DNA bases with H-bonds, which can slow the variation rates of the strengths of the H-bonding and π⋯π interactions between drug and DNA bases in the anti-cooperative process, leading to the intercalation formation. The enthalpy change is the major factor driving the positive thermodynamic cooperativity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...