Halogen bonding in differently charged complexes: basic profile, essential interaction terms and intrinsic σ-hole†
Abstract
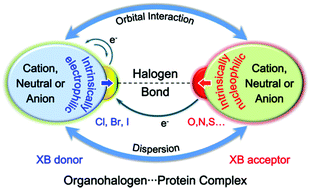
Studies on halogen bonds (XB) between organohalogens and their acceptors in crystal structures revealed that the XB donor and acceptor could be differently charged, making it difficult to understand the nature of the interaction, especially the negatively charged donor's electrophilicity and positively charged acceptor's nucleophilicity. In this paper, 9 XB systems mimicking all possibly charged halogen bonding interactions were designed and explored computationally. The results revealed that all XBs could be stable, with binding energies after removing background interaction as strong as −1.2, −3.4, and −8.3 kcal mol−1 for Cl, Br, and I involved XBs respectively. Orbital and dispersion interactions are found to be always attractive while unidirectional intermolecular electron transfer from a XB acceptor to a XB donor occurs in all XB complexes. These observations could be attributed to the intrinsic σ-hole of the XB donor and the intrinsic electronic properties of the XB acceptor regardless of their charge states. Intramolecular charge redistribution inside both the donor and the acceptor is found to be system-dependent but always leads to a more stable XB. Accordingly, this study demonstrates that the orbital-based origin of halogen bonds could successfully interpret the complicated behaviour of differently charged XB complexes, while electrostatic interaction may dramatically change the overall bonding strength. The results should further promote the application of halogens in all related areas.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...