Conformational preference and cationic structure of 2-methylpyrazine by VUV-MATI spectroscopy and natural bond orbital analysis
Abstract
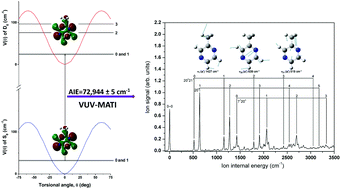
Alkylpyrazines, which are well-known as aromatic substances and traditional medicines, are interesting molecular systems, and their methyl conformations result in unique structural and dynamical properties. We explored the conformational preference of the methyl group and the highest occupied molecular orbitals (HOMOs) of 2-methylpyrazine and its cation by utilizing high-resolution one-photon vacuum ultraviolet mass-analyzed threshold ionization (VUV-MATI) spectroscopy and natural bond orbital analysis to understand the relevant molecular activities. The measured VUV-MATI spectrum of 2-methylpyrazine revealed its adiabatic ionization energy and the vibrational frequencies of its cation. From the 0–0 band in the MATI spectrum under the zero-field limit, the accurate adiabatic ionization energy was determined as 9.0439 ± 0.0006 eV (72 944 ± 5 cm−1), which is lower than that of pyrazine. The peaks observed in the spectrum were unambiguously assigned based on vibrational frequencies and Franck–Condon factors from quantum chemical calculations for individual totally symmetric transitions between the S0 and D0 states using the simple one-photon dipole selection rules. The most convincing molecular structure of the 2-methylpyrazine cation was determined by Franck–Condon fit spectral simulations. Upon removal of an electron from the non-bonding orbital (HOMO) on the para nitrogen atoms, a significant structural change takes place along the vibrational motion associated with ring distortion by contraction of the N–N distance, resulting in prominent overtones and combination bands. In addition, the methyl substitution of pyrazine lowered the adiabatic ionization energy and the methyl group preferred the anti-configuration with respect to the pyrazine moiety in the D0 state, resulting in a frozen internal rotation regardless of ionization.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2019 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...