The potential application of black and blue phosphorene as cathode materials in rechargeable aluminum batteries: a first-principles study†
Abstract
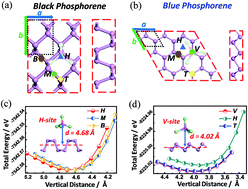
Developing a suitable cathode material for rechargeable aluminum-ion batteries (AIBs) is currently recognized as a key challenge in pushing AIBs from lab-level to industrial application. Herein, detailed density functional theory (DFT) calculations are carried out to investigate the potential application of black and blue phosphorus monolayers as cathode materials for AIBs. It can be found that AlCl4− ions can strongly bind with both phosphorene allotropes, along with significant charge transfer. For black P, a semiconducting-to-metallic transition is realized in the (AlCl4)8P16 compound. Likewise, the band gap of blue P is reduced from 1.971 eV (pristine blue P) to 0.817 eV. Moreover, both phosphorene allotropes show excellent structural integrity with increased AlCl4− concentration, while delivering competitive theoretical capacities of 432.29 and 384.25 mA h g−1 for black ((AlCl4)8P16) and blue phosphorene ((AlCl4)8P18), respectively. Kinetic calculations present modest energy barriers of 0.19 and 0.39 eV for AlCl4− ions migrating on the surface of black and blue P, and an anisotropic migration nature is also found in both phosphorene allotropes. Based on our results, black and blue phosphorene show great potential as cathode materials for AIBs with robust ion-adsorption, insignificant deformation, self-improved conductivity, and fast kinetic performance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...