A comparison between hydrogen and halogen bonding: the hypohalous acid–water dimers, HOX⋯H2O (X = F, Cl, Br)†
Abstract
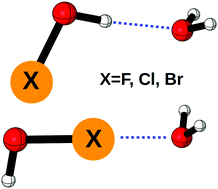
Hypohalous acids (HOX) are a class of molecules that play a key role in the atmospheric seasonal depletion of ozone and have the ability to form both hydrogen and halogen bonds. The interactions between the HOX monomers (X = F, Cl, Br) and water have been studied at the CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ level of theory with the spin free X2C-1e method to account for scalar relativistic effects. Focal point analysis was used to determine CCSDT(Q)/CBS dissociation energies. The anti hydrogen bonded dimers were found with interaction energies of −5.62 kcal mol−1, −5.56 kcal mol−1, and −4.97 kcal mol−1 for X = F, Cl, and Br, respectively. The weaker halogen bonded dimers were found to have interaction energies of −1.71 kcal mol−1 and −3.03 kcal mol−1 for X = Cl and Br, respectively. Natural bond orbital analysis and symmetry adapted perturbation theory were used to discern the nature of the halogen and hydrogen bonds and trends due to halogen substitution. The halogen bonds were determined to be weaker than the analogous hydrogen bonds in all cases but close enough in energy to be relevant, significantly more so with increasing halogen size.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 1st International Conference on Noncovalent Interactions


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
