Tannic acid capped gold nanoparticles: capping agent chemistry controls the redox activity†
Abstract
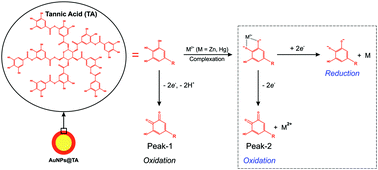
We report the key role of the capping agent in the detection of metal cations using tannic acid (TA) capped gold nanoparticles at both ensembles (using cyclic voltammetry) and with individual particles (using oxidative and reductive nanoimpacts). The results show that the capping agent complexes with Zn2+ and Hg2+ in a reversible and Langmuirian manner in both cases. The sensitivity of detection is determined by the amount of capping agent present on the nanoparticles with similar values seen for both oxidation and reduction reactions. The optimisation of the capping agent loading is therefore key to metal ion detection.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...