Rotational (de)-excitation of linear C3O by collision with He†
Abstract
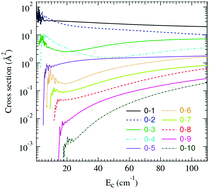
Tricarbon monoxide (C3O) is an astrochemically important molecule. It is a probe element for determining the chemical composition of gases in molecular clouds, as C3O is a major intermediate of ion-molecule reactions in the gas phase. For C3O, no collision coefficients are available in the literature. To estimate the abundance of C3O in a solar cold dark cloud: Taurus Molecular Cloud 1 (TMC-1) and find the range of cloud parameters, some authors used the calculated values for the HC3N molecule, which is isoelectronic and has similar rotational constants. Indeed, the calculation of the rate coefficients of C3O(1Σ+) induced by collision with He is performed for thermal temperatures below 25 K. These calculations are based on a new two-dimensional potential energy surface obtained from the explicitly correlated coupled cluster with a single, double and perturbative triple excitation (ccsd(t)-f12) ab initio approach associated with aug-cc-pVTZ basis sets. The PES was found to have a global minimum at (R = 6.2 Bohr and θ = 73°) with a depth of −53.4 cm−1 below the C3O–He dissociation limit. Using this PES, the integral cross sections are performed in the close-coupling quantum time independant formalism for Ec ≤ 110 cm−1 and J ≤ 12. These cross sections were then averaged at low temperature to obtain the downward rate coefficients. The new collisional data should significantly help the interpretation of interstellar C3O emission lines observed with current and future telescopes. We expect that they will allow the accurate determination of the C3O abundance in the interstellar medium, which is crucial to understand the chemistry of carbon chain species in the interstellar gas.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...