The influence of antenna and anchoring moieties on the improvement of photoelectronic properties in Zn(ii)–porphyrin–TiO2 as potential dye-sensitized solar cells†
Abstract
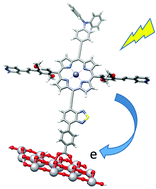
A systematic study for the rational design of porphyrins (P4 spider-shaped derivatives) with potential application in dye-sensitized solar cells is presented. Using density functional theory (DFT) (B3LYP/6-31G*) and time-dependent DFT (M06/6-31G*) we show that the UV-vis absorption properties of a spider-shaped Zn(II) porphyrin, previously synthesized by Stangel et al., may be greatly improved by applying some push–pull strategies in meso positions. We found that the selected triphenylamine push group induces a remarkable improvement in the absorption bands of P4 spider-shaped derivatives. The pull effect reached through the π-electron-rich phenyl group and the benzodithiazole (BTD) group allowed the Q bands to be red-shifted up to 689 nm, much longer than the 593 nm reported experimentally for the original spider-shaped porphyrin. The adsorption results of the P4 spider-shaped derivatives onto a TiO2-anatase surface model [Ti16O34H4] through the carboxylic acid group showed that the adsorptions energies were favourable and very similar in all cases. Natural bond orbitals (NBO) indicated a two-center bond (BD) O(carboxyl)–Ti(TiO2) for the porphyrin with the highest adsorption energy (8.27 kcal mol−1), and donor acceptor interactions from LP O(carboxyl) to Ti(TiO2) for the other porphyrins. The natural transition orbitals (NTO) for P4-derivatives-TiO2 confirm the nature of the excited states associated with Q and Soret bands. Finally, the frontier molecular orbitals revealed charge-separated states between those occupied and unoccupied, indicating a favourable charge-transfer process between the dyes and the surface conduction bands. In conclusion, this work showed a systematic study based on the push–pull strategy that improves the performance of porphyrins with the purpose to be used in dye-sensitized solar cells.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Celebrating Latin American Talent in Chemistry


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...