High hydrogen evolution activity and suppressed H2O2 production on Pt-skin/PtFe alloy nanocatalysts for proton exchange membrane water electrolysis†
Abstract
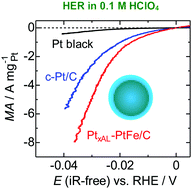
We, for the first time, demonstrate high electrocatalytic activity for the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) on PtFe alloy nanoparticles with stabilized Pt-skin layers supported on carbon black (PtxAL–PtFe/C), which allows the reduction of Pt loading to be lowered to 1/20 compared with a conventional Pt black cathode in proton exchange membrane water electrolysis (PEMWE). The area-specific HER activity of PtxAL–PtFe/C was found to be ca. 2 times higher than that of commercial Pt/C at 80 °C and −0.02 V vs. RHE. PtxAL–PtFe/C exhibited the additional important advantage of suppressed H2O2 production during the HER in the presence of O2, which inevitably diffuses from the anode in PEMWE. Both the excellent HER performance and low H2O2 production are attributed to the lower adsorption energies of atomic hydrogen on Pt-skin surfaces, as revealed by DFT calculations.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...