The adhesion energy measured by a stress accumulation-peeling mechanism in the exfoliation of graphite†
Abstract
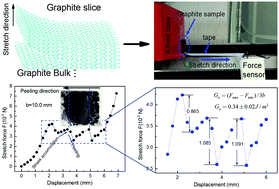
The mechanical exfoliation of graphite using tape is one way to obtain high-quality graphene samples. However, the amount of graphene obtained is negligible due to the unclear exfoliation mechanism. In this paper, we present a stress accumulation-peeling mechanism, which can be applied to measure the adhesion energy of graphite. This mechanism is different from a wriggle or a creep. First, we obtained a simple universal formula to measure the adhesion energy Ga = (Fmax − Fmin)/3b, where Fmax and Fmin are the maximum and minimum values, respectively, of the external stretch force in the peeling process, and b is the width of the peeling arm. Second, the reliability of the method was demonstrated by measuring the adhesion energy between polydimethylsiloxane and glass. Using the simple universal formula, the adhesion energies of three graphite slices were determined to be 0.34 ± 0.03, 0.33 ± 0.06 and 0.34 ± 0.02 J m−2. These adhesion energies were consistent with the other measured result of 0.33 J m−2, which was based on the self-retraction phenomenon of graphite. The macroscopic method is very simple and easy to implement. It can be used to measure the adhesion energy of any van der Waals material and any biomaterial with adhesion interaction, as well as prepare excellent 2D material samples by optimizing the experimental conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...