Theoretical evaluation of thermal decomposition of dichlorosilane for plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition of silicon nitride: the important role of surface hydrogen†
Abstract
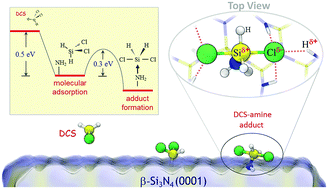
Silicon nitride (SiN) thin films have been widely employed for various applications including microelectronics, but their deposition presents a challenge especially when highly conformal layers are necessary on nanoscale features with high aspect ratios. Plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD) has been demonstrated to be a promising technique for controlled growth of SiN thin films at relatively low temperatures (<400 °C), in which thermal decomposition of Si-containing precursors on a N-rich surface is a critical step. Based on periodic density functional theory calculations, we present potential underlying mechanisms leading to facile thermal decomposition of dichlorosilane (DCS, SiH2Cl2) on the N-rich β-Si3N4(0001) surface. Our study highlights the importance of high hydrogen content on the N-rich surface, rendering primary and secondary amine groups. When the N-rich β-Si3N4(0001) surface is fully hydrogenated, the molecular adsorption of DCS is predicted to be exothermic by 0.6 eV. In this case, DCS decomposition appears to be initiated by nucleophilic attack by an amine lone-pair on the electrophilic Si, leading to the formation of a DCS-amine adduct intermediate followed by release of a Cl− anion and a proton. The predicted activation barrier for the DCS decomposition reaction is only 0.3 eV or less, depending on its adsorption configuration. We also discuss the formation and desorption of HCl, the subsequent formation and nature of Si–N bonds, and the interaction between adsorbed DCS molecules. While clearly demonstrating the advantageous features of DCS as a Si precursor, this work suggests that the thermal decomposition of Si precursors, and in turn the ALD kinetics and resulting film quality, can be strongly influenced by surface functional groups, in addition to product accumulation and precursor coverage.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...