Local crystal structure and mechanical properties of sputtered Ti-doped AlN thin films
Abstract
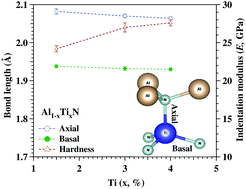
In this article, we predominantly report the investigation of the local crystal structure around a Ti dopant by X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) and the nano-mechanical properties of co-sputtered Al1−xTixN (x = 0 to 4%) thin films. Grazing incidence X-ray diffraction (GIXRD) results show that these films are crystallized with the hexagonal wurtzite structure of AlN. Surface chemical analysis and morphology analysis of Al1−xTixN films are executed using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and atomic force microscopy (AFM) techniques, respectively. X-ray absorption near-edge structure (XANES) shows that a Ti atom replaces Al in the AlN crystal and forms localized distorted tetrahedral TiN species, leading to a tensile strain. The bond lengths (Ti–N)ax and (Ti–N)bs are found to be moderately decreased with increasing Ti concentration, which is extracted from the extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) analysis. However, the Ti–Al bond length in the second coordination sphere having Al vacancies is unaffected by Ti concentration. The hardness (H) and modulus (E) of Al1−xTixN films are measured by the nano-indentation technique, and increase from 17.5 to 27.6 GPa and 231 to 293 GPa, respectively with x = 0 to 4 at% because of the improvement of p–d hybridization between the Ti and N atoms.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...