Molecular dynamics study on the heterogeneous nucleation of liquid Al–Cu alloys on different kinds of copper substrates
Abstract
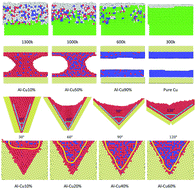
Al–Cu alloys are widely used in aeronautics and aerospace engineering because they exhibit outstanding performance. However, their casting characteristics are poor. Heterogeneous nucleation plays a significant role in controlling crystal growth. MD simulations are performed to explore the heterogeneous nucleation of liquid Al–Cu on a copper substrate including the heat-up process, preservation process, and freezing process. The simulation results show that the Al–Cu melt becomes layered at the liquid–solid interface and tends to be ordered in the structure because of the induced effect from the substrate. The crystal structure information is found to be gradually delivered from the substrate to the liquid, and this transmission capacity of information decays with increasing distance from the substrate. The liquid Al–Cu alloy with high copper content frozen on the single substrate tends to form a perfect crystal structure more easily, but the Al–Cu melt with low copper content between two copper substrates tends to form an arch-shaped structure, which can disappear when the copper content reaches a specific proportion. Moreover, different angles of the grooved substrates also affect the heterogeneous nucleation of the Al–Cu melt and its solidified structure. Our findings provide new insights into the defect and structural changes during heterogeneous nucleation, and our findings also promote leading-edge studies, which can provide new ideas to mechanical research.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...