Palladium nanoparticle formation processes in fluoropolymers by thermal decomposition of organometallic precursors
Abstract
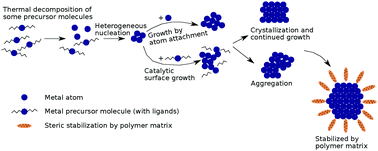
Palladium nanoparticles were synthesized directly in solid fluoropolymer films by thermal decomposition of a palladium acetylacetonate precursor molecularly infused in the fluoropolymer matrix. This chemical infusion synthesis technique was studied using transmission electron microscopy along with selective area electron diffraction to gain insight into the nucleation and growth of palladium nanoparticles. Formation of palladium nanoparticles can be correlated with defects in the polymer matrix as well as their associated free volume such that a relationship between average particle size and mean free volume fraction can be constructed. At low processing temperatures, the average particle radius increases monotonically with the processing time but more complicated variations occur for longer times. The growth of nanoparticles was interpreted using a modified diffusion-limited growth model. While nearly monodisperse nanoparticles dispersed throughout the polymer volume were obtained at low processing temperatures, surface percolation of nanoparticles was observed at relatively high temperatures owing to high precursor decomposition and diffusion rates.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
